Your Guide to Everything CBD
We want to keep you feeling informed and confident in all things CBD. Lumen CBD is committed to consumer education and want to be a resource for you. Its critical to understand WHY not all CBD products are created equally and how to choose one that’s right for you.
About CBD Oil and MCT
Encourages faster processing and use by the endocannabinoid system. This means that your body can burn those fats and put them – and the cannabinoids they hold – to use right away.
MCT oil stands for “medium chain triglyceride” oil. “long-chain triglycerides,” or LCT’s. Basically, LCT’s are much more difficult for the body to digest, metabolize, and ultimately use as an energy source than are MCT’s. In fact, rather than becoming immediately available as energy, the majority of naturally-existing fats in coconut oil (i.e. LCT’s) end up being stored rather than burned. And of course, this is not good for cardiovascular health, metabolism, and a range of other things.
Basically, medium chain triglycerides are the compounds that give “health and beauty” oils like coconut oil all of their wonderfully therapeutic and cleansing properties.
MCT’s have been documented to be very easily metabolized and consumed as energy by the body’s digestive system. They provide an almost immediate source of natural fuel, and instead of being stored in tissue as saturated fat and cholesterol-damaging lipid material, are readily taken in by cells and metabolized to provide the body with clean, ultra-efficient energy supplies.
MCT oil is a research-based, lab-only product that’s a combination of medium chain triglycerides from both coconut oil and palm oil
Why use MCT Oil?
MCT oil is a dietary supplement that is made up of MCT fats, which are fats that can be found in coconut oil, palm kernel oil, and dairy products.
MCT oil is mainly used by people looking to lose weight, or boost their endurance during a workout.
Some supporters of MCT oil also claim it can improve the ability to think, as well as help with various forms of dementia.
What are MCTs and why are they different from other fats?
Fats are made up of chains of carbon atoms, and most of the fats in a person’s diet are made up of 13 to 21 of these atoms. These are called long-chain fatty acids.
In contrast, short-chain fatty acids are made up of 6 or fewer carbon atoms.
MCTs refers to medium-chain triglycerides that sit in the middle of the other two types. They are of medium length and made up of 6 to 12 carbon atoms.
MCTs are found in coconut oil and are processed by the body in a different way to long-chain fatty acids. Unlike other fats, they go straight from the gut to the liver. From here, they are used as a source of energy or turned into ketones.
Ketones are substances produced when the liver breaks down a lot of fat, and they can be used by the brain for energy instead of glucose or sugar.
As the calories in MCTs are used straightaway, they are less likely to be stored as fat. This principle is the basis of the ketogenic diet, which many people believe is an effective way to lose weight.
Potential health benefits of MCT oil
There are several potential health benefits of MCT oil. Some of these are supported by scientific evidence, while others are yet to be proven. Each potential benefit and its available evidence is explored below:
1. Better brain and memory function
The Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation have reported the pros and cons of MCTs in respect of brain and memory function, as well as their potential benefits for those with Alzheimer’s disease.
But to what extent are the claims surrounding MCTs backed up by scientific evidence?
A 2016 review notes that in three studies, the brain’s take-up of ketones in people with Alzheimer’s was the same as in healthy people. In contrast, the brain’s take-up of glucose was poorer in those with Alzheimer’s than healthy people.
The reviewers also note that ketosis has a slight beneficial effect on thinking ability for those with Alzheimer’s. Ketosis is when the brain uses ketones for energy instead of glucose.
More research is needed to say with certainty that MCTs or MCT oil can improve brain and memory function. That said, initial research is promising, and there is growing interest in the use of MCTs in this area.
2. Energy boost and increased endurance
Supporters of MCT oil claim that it can help boost a person’s energy and improve their endurance when they are working out.
A 2009 study found that consuming food rich in MCTs, rather than longer-chain fats, improved the time that recreational athletes could endure high-intensity exercise.
This evidence is encouraging but too limited to conclude for certain that MCTs or MCT oil can improve exercise endurance, as one 2010 study notes.
3. Weight loss and improved weight management
A popular claim that supporters of MCT oil make is that it helps with weight loss. This area has been studied the most by scientists.
A 2003 study found that MCTs increased the calories and fat that overweight men burned. It concluded that MCTs might be helpful in the prevention of obesity and to stimulate weight loss.
A 2014 study found that MCTs led to a greater increase in the hormones that reduce appetite and make a person feel full. This was in comparison with longer-chain fats.
The evidence suggests that MCTs may play an important role in weight loss and management.
However, it is important to note that studies have looked at MCTs as a type of dietary fat rather than MCT oil supplements specifically.
4. Lowered cholesterol
MCTs may also have a part to play in helping to protect heart health by lowering cholesterol.
A 2009 study that looked at 40 women found that consuming coconut oil reduced bad types of cholesterol and improved good ones. The comparison was to soybean oil and taken alongside a calorie-controlled diet.
As MCT oil is high in the MCTs found in coconut oil, it is also likely to improve cholesterol levels. However, as the study did not look at MCT oil specifically, this cannot be said with certainty.
5. Lowered blood sugar levels
MCTs may also help to improve blood sugar levels and play a potential role in diabetes management.
A 2007 study found MCT improved diabetes risk factors, including insulin resistance, in a small group of participants with type 2 diabetes.
Risk and Considerations
MCTs from dietary sources and MCT oil may have some health benefits. However, it is important to remember that when a person consumes these, they are consuming fats.
Taking MCT oil adds extra fats and calories to a person’s diet. As such, excessive use of MCT oil may not be beneficial and could lead a person to gain weight.
MCT oil supplements are created from versions of food oils, and so are not considered a natural product.
It is important to remember that MCT oil has a low smoke point, so it is not suitable for cooking.
However, solid coconut oil, which is high in MCTs, can be used in cooking and may be used to replace olive oil or other cooking oils.
Your Guide to Everything CBD
We want to keep you feeling informed and confident in all things CBD. Lumen CBD is committed to consumer education and want to be a resource for you. Its critical to understand WHY not all CBD products are created equally and how to choose one that’s right for you.
Cannabichromene (CBC) is an often-overlooked cannabinoid found in cannabis. Despite being abundant in certain strains of cannabis, it’s the least studied of all major cannabinoids.
While CBC hasn’t demonstrated groundbreaking therapeutic benefits like THC or CBD, research shows that it does have pain relieving, antidepressant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, anti-anxiety, and bone and brain cell stimulating effects that can assist in the treatment of a variety of conditions.
Research has so far shown CBN may be therapeutically beneficial in the following ways:
Pain reliever – CBC has shown to have pain-relieving properties. When combined with CBD, it demonstrated effectiveness at reducing sensitivity to pain76.
Relieves symptoms of depression – CBC has shown to provide significant antidepressant-like effects when administered on its own, as well as when combined with THC38. In addition, CBC has shown to encourage new brain cell birth, in turn helping prevent the decline of growth in these cells, which is thought to contribute to disorders like depression109.
Inhibits growth of fungus – CBC has demonstrated “strong” antibacterial and antifungal effects, showing it can fight against bacteria like E. coli and staph119.
Relieves anxiety – CBC can reduce anxiety and stress levels. By interacting with CB1 receptors, CBC stimulates the release of natural chemicals that reduce the excitability of brain cells103.
Reduces inflammation – CBC has demonstrated itself as an effective anti-inflammatory agent, suggesting it could assist with inflammatory-related conditions like arthritis or cardiovascular disease34,128. In mice, it’s shown to reduce inflammation of the gastrointestinal system, indicating that could help treat Crohn’s disease or other inflammatory bowel diseases55. Its anti-inflammatory properties are not caused by interacting with cannabinoid receptors, which means CBC could possibly be combined with other cannabinoid receptor-stimulating cannabinoids that to produce even greater anti-inflammatory effects55.
Inhibits cancer growth – CBC has shown to help inhibit the uptake of anandamide, a human-produced endocannabinoid that has anti-cancer effects, allowing it to remain in the body’s system and work at fighting cancer. Cannabinoids like CBC have also shown inhibits the growth of cancerous tumors in mice, suggesting they may be used as a cancer chemopreventive agent in the future88.
Promotes bone growth – Cannabinoids, like CBC, have shown to be effective at activating human osteoclasts, thus increasing bone density and reducing the risk of bone health conditions like osteoporosis124.
Promotes growth of new brain cells – CBC has been shown to encourage neurogenesis (birth of new brain cells), an important process for memory and learning, and to increase the viability of developing brain cells. The decline of growth in these cells is thought to contribute to disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and depression109.
Cannabichromene (CBC) is an often-overlooked cannabinoid found in cannabis. Despite being abundant in certain strains of cannabis, it’s the least studied of all major cannabinoids.
While CBC hasn’t demonstrated groundbreaking therapeutic benefits like THC or CBD, research shows that it does have pain relieving, antidepressant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, anti-anxiety, and bone and brain cell stimulating effects that can assist in the treatment of a variety of conditions.
Research has so far shown CBN may be therapeutically beneficial in the following ways:
Pain reliever – CBC has shown to have pain-relieving properties. When combined with CBD, it demonstrated effectiveness at reducing sensitivity to pain76.
Relieves symptoms of depression – CBC has shown to provide significant antidepressant-like effects when administered on its own, as well as when combined with THC38. In addition, CBC has shown to encourage new brain cell birth, in turn helping prevent the decline of growth in these cells, which is thought to contribute to disorders like depression109.
Inhibits growth of fungus – CBC has demonstrated “strong” antibacterial and antifungal effects, showing it can fight against bacteria like E. coli and staph119.
Relieves anxiety – CBC can reduce anxiety and stress levels. By interacting with CB1 receptors, CBC stimulates the release of natural chemicals that reduce the excitability of brain cells103.
Reduces inflammation – CBC has demonstrated itself as an effective anti-inflammatory agent, suggesting it could assist with inflammatory-related conditions like arthritis or cardiovascular disease34,128. In mice, it’s shown to reduce inflammation of the gastrointestinal system, indicating that could help treat Crohn’s disease or other inflammatory bowel diseases55. Its anti-inflammatory properties are not caused by interacting with cannabinoid receptors, which means CBC could possibly be combined with other cannabinoid receptor-stimulating cannabinoids that to produce even greater anti-inflammatory effects55.
Inhibits cancer growth – CBC has shown to help inhibit the uptake of anandamide, a human-produced endocannabinoid that has anti-cancer effects, allowing it to remain in the body’s system and work at fighting cancer. Cannabinoids like CBC have also shown inhibits the growth of cancerous tumors in mice, suggesting they may be used as a cancer chemopreventive agent in the future88.
Promotes bone growth – Cannabinoids, like CBC, have shown to be effective at activating human osteoclasts, thus increasing bone density and reducing the risk of bone health conditions like osteoporosis124.
Promotes growth of new brain cells – CBC has been shown to encourage neurogenesis (birth of new brain cells), an important process for memory and learning, and to increase the viability of developing brain cells. The decline of growth in these cells is thought to contribute to disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and depression109.
Cannabichromene acid (CBC-a) is considered to be the fourth key cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. CBC-a is located in the most abundant levels in tropical marijuana plant strains. However, it can also be found in other strains but not at the same levels.
In recent years, specific strains of marijuana have been developed that boast higher than normal levels of CBC-a. Medical marijuana researchers and the pharmaceutical industry have found that strains with higher levels of CBC-a help fight inflammation and feature strong antibacterial properties.
MaximumYield explains Cannabichromenic Acid (CBC-a)
Cannabichromenic acid is believed to start being secreted by the cannabis plant during the plant’s early seedling stage. It appears that CBC-a develops in the young seedling before the young plant even starts to create tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Unlike THC, CBC-a is non-psychoactive and can later be converted into cannabichromene (CBC) through an aging and heating process. The heating process, known as decarboxylation or decarbing, converts the CBC-a into usable CBC, which readily binds with the human body’s C-receptors.
Cannabichromevarin (CBCV) first came to limelight in 1975 when Thailand researchers at the University of Nagasaki isolated the compound from a cannabis plant. However, not much research has been conducted on the compound since its discovery.
The concentration of CBCV in cannabis plants is much lower compared to cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). CBCV is related to cannabichromene (CBC), a compound that appears in smaller amounts than the two major ones. The chemical structure of CBCV is similar to that of CBC but much shorter. CBCV can rightly be described as a propyl cannabinoid, meaning that its molecular structure contains a propyl chain. The molecular formula for this compound is C19H26O2.
If the medical benefits of CBCV turn out to be similar to CBC, then patients may benefit from it without feeling impaired, similar to CBD. We know that CBC does not have any psychoactive effects, hence users will not feel high after taking it. However, it can relieve pain, drastically minimize inflammation, and improve upon the symptoms of depression. CBCV could make these results much stronger.
Some researchers are of the opinion that all cannabinoids in a particular strain work hand-in-hand to make the substance very potent. If this is true, then CBCV can help potentiate the therapeutic effects of other compounds
(CBCV) is a propyl cannabinoid, which means it has a propyl chain in its molecular structure. Instead of having a pentyl chain like its counterpart, cannabichromene (CBC), it branches off to have a propyl chain. This means it can have similar effects to CBC, but with a few differences,
Cannabichromevarinic Acid, being one of the major compounds in cannabinoid, target receptors in our bodies to help us in our daily functions such as appetite, sleep patterns, mood, and movement.
Unlike THC, compounds associated with CBD are popular and considered safer since they don’t have hallucination inducing properties.
Cannabichromevarinic Acid has the molecular structure – C20H26O4 and molecular weight of 330.424g/mol.
Just like Cannabichromevarin, there are numerous Cannabichromene compounds which are not supported by adequate research work to fully understand their distinctive impact on the human body. More than 80 cannabinoids have been identified so far but the role and significance of most of them have yet to be understood.
In present times, we can only categorize THC and CBD. Cannabichromevarinic Acid belongs to CBD and unlike THC, which has anti-spasmodic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-tremor, anti-emetic and appetite stimulant properties, CBD gives anti-convulsant, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-psychotic, immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effects.
Indeed, there is a lot of room for the research work on Cannabichromevarinic Acid. Currently, we hold very limited scientific information on the toxicology and pharmacology of these cannabinoids. Since these cannabinoids are quite similar in their molecular structures, they are assumed to produce same effects on the human body as that of cannabinoids.
For instance, CBD is believed to be highly impactful in suppressing muscle spasticity, bladder dysfunction, spasms and pain symptoms of MS.
CBD and its relevant compounds like Cannabichromevarinic Acid are not intoxicating. In fact, it has been postulated that CBD and its compound present in the cannabis plant may eliminate a few of the potentially unwanted THC side effects.
Cannabichromevarinic Acid and Endocannabinoid System
The only way to learn more about this Cannabichromevarinic acid is to learn about CBC’s relation with body’s endocannabinoid system. An endocannabinoid system in the human body consists of cannabinoids receptors and cannabinoids.
They work as a lock-and-key system. When these receptors unlock, it causes changes in the functionality of cells that causes different effects in the human body.
CBC does not bind properly with CB1 receptors in the brain thus it doesn’t produce any psychological effects. CBC is a highly effective painkiller. It offers antifungal and antibacterial properties, along with some antidepressant effects. It also has therapeutic effects in the treatment of diarrhea and acne.
Cannabicyclols
CBL has the molecular formula C₂₁H₃₀O₂, identical to many other cannabinoids including THC, CBD, CBC and CBG. However, all these molecules differ slightly in the arrangement of their atoms, giving them significantly different effects.
CBL itself differs from THC in that it contains no double bond within its molecule. The position of the double bond in the various isomers of THC determines how psychoactive the isomer is (Δ⁹-THC is the most psychoactive). Lacking a double bond entirely, CBL is not considered to have psychoactive potential, and it is not known if it has affinity with the cannabinoid receptors.
CBL is known to occur as a degradation product of cannabichromene (CBC). CBL has been found in samples of Pakistani hashish stored for six months to four years; all samples that contained CBL also contained CBC in higher concentrations. However, levels of both CBC and CBL were very low compared to the major constituents, THC, CBD and CBN.
CBL has also been found in an ancient sample of cannabis discovered in a Chinese tomb and dated to approximately 2700 BCE. In this sample, CBN and CBL were respectively the two largest fractions; CBD levels were much lower and THC was undetectable (although the presence of CBN and other metabolites indicates it was once high in THC).
A rare, non-intoxicating compound that originates as cannabichromenic acid (CBCA) then converts to cannabicyclolic acid (CBLA) when cannabis is exposed to natural environmental changes during storage. CBLA has been studied for its anti-inflammatory properties, among other potential benefits.
Studies show that cannabicyclolic acid (CBLA) reduces inflammation.
Cannabicyclolic acid (CBLA) comes from another compound’s degradation.
CBLV was first detected by combined gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in 1972.
Identification of cannabicyclol with a pentyl or propyl side-chain by means of combined gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
Vree TB, Breimer DD, van Ginneken CA, van Rossum JM.
J Chromatogr. 1972 Dec 6;74(1):124-7. No abstract available.
PMID: 4635939
CBLV was later isolated as optically inactive colourless needles.
CBLV structure was confirmed by comparison with synthetic CBLV-C3 obtained by irradiation of CBCV-C3.
Cannabidiols
While THC is the cannabinoid that gets most of the attention, the relatively recent monumental findings on the potential therapeutic benefits of cannabidiol (CBD) are finally giving the non-psychoactive compound its due shine.
Studies indicate that CBD safely and effectively reduces nausea and vomiting, suppresses seizure activity, combats psychosis disorders, contests inflammatory disorders, counters neurodegenerative disorders, fights tumor and cancer cells, and battles anxiety and depression disorders42,135. Because of these notable effects, CBD shows exciting potential as a treatment option for neuroinflammation disorders, epilepsy, oxidative injury, vomiting and nausea, and anxiety and schizophrenia42.
CBD has shown to potentially be beneficial for the treatment of the following diseases and disorders:
Alzheimer’s Disease – CBD limits the progression of Alzheimer’s disease by blocking microglial activation, thus providing neuroprotection19,78,104. The combination of neuroprotective, anti-oxidative, and anti-apoptotic effects provided by CBD decreases the oxidative stress associated with Alzheimer’s disease54.
Amytotraphic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) – CBD can significantly slow the onset of ALS127. In addition, it can help reduce the pain, appetite loss, depression, sleeping problems, spasticity, and drooling that can are commonly associated with ALS3,22.
Anxiety Disorder – CBD has effects on the limbic and paralimbic areas of the brain that reduce anxiety and significantly decreases subjective anxiety30. It’s also been shown to significantly reduce the anxiety, cognitive impairment, and discomfort associated with public speaking in individuals with Generalized Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)12.
Arthritis – With its anti-inflammatory benefits and potent anti-arthritic effects that protect joints, CBD limits the progression of arthritis77.
Bone Health – CBD enhances the maturation of collagen, the protein in the bone’s connective tissue that holds the bone together, to significantly improve the strength and the healing process of bones60.
Cancer – CBD has shown to inhibit the progression of cancers located in the breast, lung, prostate and colon in animal models, suggesting it could also be effective at mediating cancer cell death in human subjects69,81,93. In one study, it inhibited human breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion, and decreased the gene expression in cancer cells, thus lowering the tumor’s aggressiveness and significantly reducing its size79. CBD acid (CBDA) has shown the capability of down-regulating invasive human brain cancer cells and therefore preventing their growth80,116.
Cardiovascular Disease – CBD reduces myocardial dysfunction, cardiac fibrosis, oxidative-nitrative stress, inflammation, cell death, and interrelated signaling pathways, which collectively offer therapeutic benefits in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases101. In addition, administering CBD shortly after a heart attack has been shown to reduce infarct size and myocardial inflammation, thus showing potential as a treatment for myocardial ischemia37.
Cirrhosis (Liver Disease) – Studies suggest that CBD helps combat the progression of cirrhosis by assisting in the death of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which proliferate and produce excess collagen, causing the accumulation of scarring on the liver70. CBD has also been shown to restore liver function in mice experiencing liver failure7. In addition, CBD provides protection against ischemia reperfusion, the pivotal mechanism of tissue damage in cirrhosis, by reducing the force of key inflammatory pathways and oxidative/nitrative tissue injury84.
Crohn’s Disease (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) – CBD encourages anti-inflammation of the digestive track by controlling the pro-inflammatory response caused by the disease33,40.
Depression – CBD has demonstrated both antidepressant and anti-anxiety effects in animal models35,131.
Diabetes – CBD has shown to significantly reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines in the bloodstream and the incidence of diabetes in non-obese mice125. It’s also been shown to be effective at curtailing the manifestations of the disease126. Research has found CBD treatments provide significant protection from diabetic retinopathy39.
Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders – CBD has demonstrated the ability to reduce or even eliminate seizures15,36,107,114. Research also finds that cannabis is effective in the treatment of severe pediatric epilepsy disorders like Dravet syndrome, Doose syndrome, and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome98. CBD has also been shown to improve sleep (53%), alertness (71%), and mood (63%) in epileptic children50.
Leukemia – CBD helps prevent complications that can occur after a leukemia patient receives a stem cell or bone marrow transplant129. In addition, it has been found to help cancer patients manage the nausea, vomiting, pain, and appetite suppression associated with traditional cancer treatments.
Migraines – CBD is effective at reducing pain associated with a wide variety of conditions, including headache and migraines10<s/up>.
Multiple Sclerosis – CBD combats the inflammation associated with multiple sclerosis, therefore providing neuroprotection and limiting the disease’s progression62,82. CBD effectively reduces the spasticity caused by multiple sclerosis28. In addition, it has demonstrated the ability to reduce the neuropathic pain associated with multiple sclerosis9.
Nausea – Studies have found that cannabinoids, including CBD, are effective at treating the more difficult to control symptoms of nausea, as well as preventing anticipatory nausea in chemotherapy patients94.
Obesity – CBD has been shown to significant decrease body weight gain and reduce lipid levels53,112.
Pain – CBD has been shown effective at lowering pain levels associated with a wide variety of conditions, including spasticity, headache, migraines, and other acute pain and chronic pain conditions10,57.
Parkinson’s Disease – CBD has neuroprotective properties and supports the health of neural cells mitochondria, thus helping to prevent neurodegeneration32,42,134. Significant improvements in well being and quality of life scores were found in Parkinson’s disease patients undergoing CBD treatment25. CBD may help Parkinson’s disease patients experiencing psychosis134.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) – CBD’s interaction with the cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) modulates the release of neurotransmitter that increases a sense of pleasure and initiates alternation of memory processes13. CBD can also block the continuous retrieval of the traumatic event, thus enhancing its extension and reducing its associated anxiety2,95,117.
Schizophrenia – CBD has anxiolytic and antipsychotic properties. Schizophrenia patients treated with CBD in trials have shown that CBD is a safe and well-tolerated alternative treatment for schizophrenia68,133.
Sickle Cell Anemia – Cannabinoids have shown to be effective at helping curtail the severe pain associated with sickle cell disease49,61.
Spinal Cord Disease – CBD improves bladder control, muscle spasms, and spasticity in patients with spinal cord diseases and damage121.
Spinal Cord Injuries – When administered shortly after a spinal cord injury, CBD stimulates a neuroprotective response to limit damage6. CBD has shown to improve motor scores following a spinal cord injury64.
Stroke – Administering CBD shortly after a stroke protects neurons and astrocytes from damage, and therefore leads to improved functional, histological, biochemical, and neurobehavior recovery65.
Traumatic Brain Injury – CBD has shown to provide a neuroprotective effect and limit brain damage following a traumatic brain injury23,83,96.
Cannabinol monomethyl ether an analytical reference standard that is categorized as a phytocannabinoid. It can be isolated from Cannabis plants, derived from cannabinol, or synthesized.1,2,3 The physiological and toxicological properties of this compound are not well known.
Definition – What does Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDA) mean?
Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) occurs in the resin glands (trichomes) of the cannabis plant. It is the precursor of cannabidiol (CBD).
CBDA is considered inactive until it is activated and then it becomes active CBD. To activate CBDA, it must be aged and go through a heating process (decarboxylation) to convert it to CBD.
Heat causes the acid molecules of CBDA to break down and become activated CBD. CBDA is found in strains of cannabis that boast high levels of CBD.
MaximumYield explains Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDA)
Cannabis concentrates with high levels of CBD have become popular with medicinal marijuana users. Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) has no psychoactive effects when consumed. However, it is believed to have numerous health benefits.
Medicinal marijuana plants are frequently cultivated that boast high levels of CBD with very little or no THC. CBD has been proven effective at treating many medical conditions such as epilepsy. Strains of marijuana such as Charlotte’s Web offer high levels of CBDA, which, through decarbing can be converted to CBD to treat epilepsy and nausea from cancer treatment medications.
Many varieties of industrial hemp also have high levels of CBDA. Unlike cannabis plants that feature exceedingly high levels of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), most marijuana plants have less than 5 per cent CBD.
CBD-C1 is beneficial to relieve pain and reduce inflammation, requiring a lower dosage than other CBD counterparts
is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in Cannabis. It is a homolog of cannabidiol (CBD), with the side-chain shortened by two methylene bridges (CH2 units). Plants with relatively high levels of CBDV have been reported in feral populations of C. indica ( = C. sativa ssp. indica var. kafiristanica) from northwest India, and in hashish from Nepal.[1][2] CBDV has anticonvulsant effects.[3]
Similarly to CBD, it has 7 double bond isomers and 30 stereoisomers (see: Cannabidiol#Double bond isomers and their stereoisomers). It is not scheduled by Convention on Psychotropic Substances. It is being actively developed by GW Pharmaceuticals[4] (as GWP42006) because of a demonstrated neurochemical pathway for previously-observed anti-epileptic and anti-convulsive action.[5] GW has begun a phase 2 trial for adult epilepsy,[6] and is to begin trials of this CBDV product in children in 2016 in Australia.
General description
Cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in Cannabis that reportedly has anti-inflammatory properties. This certified Snap-N-Spike® solution is suitable for CBDVA testing methods by GC/MS, LC/MS or HPLC for applications in testing of Cannabis potency or impurity profiling and pharmaceutical research. Cerilliant solution Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) of cannabinoids are supplied in a convenient, quantitative, US DEA-exempt solution format and with TK#s for Canadian customers.
Legal Information
CERILLIANT is a registered trademark of Cerilliant Corporation
Snap-N-Spike is a registered trademark of Cerilliant Corporation
The chemical structure of this molecule has the atoms arrangement and the chemical bonds which hold atoms together. The molecule of Cannabidivarinic acid contains 51 bonds. It has 25 non-H bonds, 5 rotatable bonds, 9 multiple bonds, 6 aromatic bonds, 3 double bonds, 1 carboxylic acid (aromatic), 2 six-membered rings, 2 aromatic hydroxyls and 1 hydroxyl groups. The carbon atoms present in the Cannabidivarinic acid’s chemical structure are implied to be present at the corners whereas hydrogen atoms linked to carbon atoms are not indicated. Every carbon atom is generally considered to be linked with enough hydrogen atoms to offer carbon atom, at least four bonds. The information of the bonds, atoms, coordinates, and connectivity included in the Cannabidivarinic acid chemical structure can be identified easily. Since Cannabidivarinic acid is a cannabinoid, it is likely to contain the basic properties of cannabinoid. The proper research in terms of specific chemical properties of Cannabidivarinic acid is yet to be researched. Until now we don’t have enough information about the compound and its properties, which makes it difficult to identify individual properties.
Cannabielsoins
BEA-B Cannabielsoic acid B has the molecular formula C22H30O5 and molecular weight of 374.477g/mol. CBEA-B has shown promise in alleviating symptoms associated with depression, social anxiety, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
CBEA-B has shown promise in alleviating symptoms associated with depression, social anxiety, mul Doesn’t cause euphoria, but will minimize depressive behavior, reduces pain, and relieves anxiety.tiple sclerosis, epilepsy, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
The cannabinoid compound has the chemical formula of C22H30O5. It has the molecular weight of 374.4706 g/mol.
The chemical structure of Cannabielsoic acid A molecule involves the atoms arrangement and the chemical bonds that keep and hold atoms together. The molecule of Cannabielsoic acid A contains a total of 59 bonds.
In the complete one molecule of Cannabielsoic acid A, there are around 29 non-H bonds, 6 rotatable bonds, 8 multiple bonds, 6 aromatic bonds, 2 double bonds, 2 six-membered rings, 1 five-membered rings, 1 carboxylic acid(s) – aromatic, 2 nine-membered ring, 2 hydroxyl groups, 1 tertiary alcohols, 1 aromatic hydroxyl and 1 ether – aromatic.
If you look at the 2D chemical structure of Cannabielsoic acid A, it is also known as a skeletal formula. This is the standard notation in terms of organic molecules. The carbon atoms present in the Cannabielsoic acid A chemical structure are implied to be present at the corners.
The hydrogen atoms linked to carbon atoms are not indicated. In other words, each carbon atom is required to be associated with sufficient hydrogen atoms to offer the carbon atom with 4 bonds.
We do have all the chemical and molecular information about Cannabielsoic Acid A but we still lack a lot of information about the compound. We haven’t done the required research to know the medicinal effects of the compound on the human body just like other compounds present in the cannabis.
Cannabidiols
While THC is the cannabinoid that gets most of the attention, the relatively recent monumental findings on the potential therapeutic benefits of cannabidiol (CBD) are finally giving the non-psychoactive compound its due shine.
Studies indicate that CBD safely and effectively reduces nausea and vomiting, suppresses seizure activity, combats psychosis disorders, contests inflammatory disorders, counters neurodegenerative disorders, fights tumor and cancer cells, and battles anxiety and depression disorders42,135. Because of these notable effects, CBD shows exciting potential as a treatment option for neuroinflammation disorders, epilepsy, oxidative injury, vomiting and nausea, and anxiety and schizophrenia42.
CBD has shown to potentially be beneficial for the treatment of the following diseases and disorders:
Alzheimer’s Disease – CBD limits the progression of Alzheimer’s disease by blocking microglial activation, thus providing neuroprotection19,78,104. The combination of neuroprotective, anti-oxidative, and anti-apoptotic effects provided by CBD decreases the oxidative stress associated with Alzheimer’s disease54.
Amytotraphic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) – CBD can significantly slow the onset of ALS127. In addition, it can help reduce the pain, appetite loss, depression, sleeping problems, spasticity, and drooling that can are commonly associated with ALS3,22.
Anxiety Disorder – CBD has effects on the limbic and paralimbic areas of the brain that reduce anxiety and significantly decreases subjective anxiety30. It’s also been shown to significantly reduce the anxiety, cognitive impairment, and discomfort associated with public speaking in individuals with Generalized Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)12.
Arthritis – With its anti-inflammatory benefits and potent anti-arthritic effects that protect joints, CBD limits the progression of arthritis77.
Bone Health – CBD enhances the maturation of collagen, the protein in the bone’s connective tissue that holds the bone together, to significantly improve the strength and the healing process of bones60.
Cancer – CBD has shown to inhibit the progression of cancers located in the breast, lung, prostate and colon in animal models, suggesting it could also be effective at mediating cancer cell death in human subjects69,81,93. In one study, it inhibited human breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion, and decreased the gene expression in cancer cells, thus lowering the tumor’s aggressiveness and significantly reducing its size79. CBD acid (CBDA) has shown the capability of down-regulating invasive human brain cancer cells and therefore preventing their growth80,116.
Cardiovascular Disease – CBD reduces myocardial dysfunction, cardiac fibrosis, oxidative-nitrative stress, inflammation, cell death, and interrelated signaling pathways, which collectively offer therapeutic benefits in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases101. In addition, administering CBD shortly after a heart attack has been shown to reduce infarct size and myocardial inflammation, thus showing potential as a treatment for myocardial ischemia37.
Cirrhosis (Liver Disease) – Studies suggest that CBD helps combat the progression of cirrhosis by assisting in the death of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which proliferate and produce excess collagen, causing the accumulation of scarring on the liver70. CBD has also been shown to restore liver function in mice experiencing liver failure7. In addition, CBD provides protection against ischemia reperfusion, the pivotal mechanism of tissue damage in cirrhosis, by reducing the force of key inflammatory pathways and oxidative/nitrative tissue injury84.
Crohn’s Disease (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) – CBD encourages anti-inflammation of the digestive track by controlling the pro-inflammatory response caused by the disease33,40.
Depression – CBD has demonstrated both antidepressant and anti-anxiety effects in animal models35,131.
Diabetes – CBD has shown to significantly reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines in the bloodstream and the incidence of diabetes in non-obese mice125. It’s also been shown to be effective at curtailing the manifestations of the disease126. Research has found CBD treatments provide significant protection from diabetic retinopathy39.
Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders – CBD has demonstrated the ability to reduce or even eliminate seizures15,36,107,114. Research also finds that cannabis is effective in the treatment of severe pediatric epilepsy disorders like Dravet syndrome, Doose syndrome, and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome98. CBD has also been shown to improve sleep (53%), alertness (71%), and mood (63%) in epileptic children50.
Leukemia – CBD helps prevent complications that can occur after a leukemia patient receives a stem cell or bone marrow transplant129. In addition, it has been found to help cancer patients manage the nausea, vomiting, pain, and appetite suppression associated with traditional cancer treatments.
Migraines – CBD is effective at reducing pain associated with a wide variety of conditions, including headache and migraines10<s/up>.
Multiple Sclerosis – CBD combats the inflammation associated with multiple sclerosis, therefore providing neuroprotection and limiting the disease’s progression62,82. CBD effectively reduces the spasticity caused by multiple sclerosis28. In addition, it has demonstrated the ability to reduce the neuropathic pain associated with multiple sclerosis9.
Nausea – Studies have found that cannabinoids, including CBD, are effective at treating the more difficult to control symptoms of nausea, as well as preventing anticipatory nausea in chemotherapy patients94.
Obesity – CBD has been shown to significant decrease body weight gain and reduce lipid levels53,112.
Pain – CBD has been shown effective at lowering pain levels associated with a wide variety of conditions, including spasticity, headache, migraines, and other acute pain and chronic pain conditions10,57.
Parkinson’s Disease – CBD has neuroprotective properties and supports the health of neural cells mitochondria, thus helping to prevent neurodegeneration32,42,134. Significant improvements in well being and quality of life scores were found in Parkinson’s disease patients undergoing CBD treatment25. CBD may help Parkinson’s disease patients experiencing psychosis134.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) – CBD’s interaction with the cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) modulates the release of neurotransmitter that increases a sense of pleasure and initiates alternation of memory processes13. CBD can also block the continuous retrieval of the traumatic event, thus enhancing its extension and reducing its associated anxiety2,95,117.
Schizophrenia – CBD has anxiolytic and antipsychotic properties. Schizophrenia patients treated with CBD in trials have shown that CBD is a safe and well-tolerated alternative treatment for schizophrenia68,133.
Sickle Cell Anemia – Cannabinoids have shown to be effective at helping curtail the severe pain associated with sickle cell disease49,61.
Spinal Cord Disease – CBD improves bladder control, muscle spasms, and spasticity in patients with spinal cord diseases and damage121.
Spinal Cord Injuries – When administered shortly after a spinal cord injury, CBD stimulates a neuroprotective response to limit damage6. CBD has shown to improve motor scores following a spinal cord injury64.
Stroke – Administering CBD shortly after a stroke protects neurons and astrocytes from damage, and therefore leads to improved functional, histological, biochemical, and neurobehavior recovery65.
Traumatic Brain Injury – CBD has shown to provide a neuroprotective effect and limit brain damage following a traumatic brain injury23,83,96.
Cannabinol monomethyl ether an analytical reference standard that is categorized as a phytocannabinoid. It can be isolated from Cannabis plants, derived from cannabinol, or synthesized.1,2,3 The physiological and toxicological properties of this compound are not well known.
Definition – What does Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDA) mean?
Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) occurs in the resin glands (trichomes) of the cannabis plant. It is the precursor of cannabidiol (CBD).
CBDA is considered inactive until it is activated and then it becomes active CBD. To activate CBDA, it must be aged and go through a heating process (decarboxylation) to convert it to CBD.
Heat causes the acid molecules of CBDA to break down and become activated CBD. CBDA is found in strains of cannabis that boast high levels of CBD.
MaximumYield explains Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDA)
Cannabis concentrates with high levels of CBD have become popular with medicinal marijuana users. Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) has no psychoactive effects when consumed. However, it is believed to have numerous health benefits.
Medicinal marijuana plants are frequently cultivated that boast high levels of CBD with very little or no THC. CBD has been proven effective at treating many medical conditions such as epilepsy. Strains of marijuana such as Charlotte’s Web offer high levels of CBDA, which, through decarbing can be converted to CBD to treat epilepsy and nausea from cancer treatment medications.
Many varieties of industrial hemp also have high levels of CBDA. Unlike cannabis plants that feature exceedingly high levels of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), most marijuana plants have less than 5 per cent CBD.
CBD-C1 is beneficial to relieve pain and reduce inflammation, requiring a lower dosage than other CBD counterparts
Is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in Cannabis. It is a homolog of cannabidiol (CBD), with the side-chain shortened by two methylene bridges (CH2 units). Plants with relatively high levels of CBDV have been reported in feral populations of C. indica ( = C. sativa ssp. indica var. kafiristanica) from northwest India, and in hashish from Nepal.[1][2] CBDV has anticonvulsant effects.[3]
Similarly to CBD, it has 7 double bond isomers and 30 stereoisomers (see: Cannabidiol#Double bond isomers and their stereoisomers). It is not scheduled by Convention on Psychotropic Substances. It is being actively developed by GW Pharmaceuticals[4] (as GWP42006) because of a demonstrated neurochemical pathway for previously-observed anti-epileptic and anti-convulsive action.[5] GW has begun a phase 2 trial for adult epilepsy,[6] and is to begin trials of this CBDV product in children in 2016 in Australia.
General description
Cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in Cannabis that reportedly has anti-inflammatory properties. This certified Snap-N-Spike® solution is suitable for CBDVA testing methods by GC/MS, LC/MS or HPLC for applications in testing of Cannabis potency or impurity profiling and pharmaceutical research. Cerilliant solution Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) of cannabinoids are supplied in a convenient, quantitative, US DEA-exempt solution format and with TK#s for Canadian customers.
Legal Information
CERILLIANT is a registered trademark of Cerilliant Corporation
Snap-N-Spike is a registered trademark of Cerilliant Corporation
The chemical structure of this molecule has the atoms arrangement and the chemical bonds which hold atoms together. The molecule of Cannabidivarinic acid contains 51 bonds. It has 25 non-H bonds, 5 rotatable bonds, 9 multiple bonds, 6 aromatic bonds, 3 double bonds, 1 carboxylic acid (aromatic), 2 six-membered rings, 2 aromatic hydroxyls and 1 hydroxyl groups. The carbon atoms present in the Cannabidivarinic acid’s chemical structure are implied to be present at the corners whereas hydrogen atoms linked to carbon atoms are not indicated. Every carbon atom is generally considered to be linked with enough hydrogen atoms to offer carbon atom, at least four bonds. The information of the bonds, atoms, coordinates, and connectivity included in the Cannabidivarinic acid chemical structure can be identified easily. Since Cannabidivarinic acid is a cannabinoid, it is likely to contain the basic properties of cannabinoid. The proper research in terms of specific chemical properties of Cannabidivarinic acid is yet to be researched. Until now we don’t have enough information about the compound and its properties, which makes it difficult to identify individual properties.
Cannabielsoins
BEA-B Cannabielsoic acid B has the molecular formula C22H30O5 and molecular weight of 374.477g/mol. CBEA-B has shown promise in alleviating symptoms associated with depression, social anxiety, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
CBEA-B has shown promise in alleviating symptoms associated with depression, social anxiety, mul Doesn’t cause euphoria, but will minimize depressive behavior, reduces pain, and relieves anxiety.tiple sclerosis, epilepsy, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
The cannabinoid compound has the chemical formula of C22H30O5. It has the molecular weight of 374.4706 g/mol.
The chemical structure of Cannabielsoic acid A molecule involves the atoms arrangement and the chemical bonds that keep and hold atoms together. The molecule of Cannabielsoic acid A contains a total of 59 bonds.
In the complete one molecule of Cannabielsoic acid A, there are around 29 non-H bonds, 6 rotatable bonds, 8 multiple bonds, 6 aromatic bonds, 2 double bonds, 2 six-membered rings, 1 five-membered rings, 1 carboxylic acid(s) – aromatic, 2 nine-membered ring, 2 hydroxyl groups, 1 tertiary alcohols, 1 aromatic hydroxyl and 1 ether – aromatic.
If you look at the 2D chemical structure of Cannabielsoic acid A, it is also known as a skeletal formula. This is the standard notation in terms of organic molecules. The carbon atoms present in the Cannabielsoic acid A chemical structure are implied to be present at the corners.
The hydrogen atoms linked to carbon atoms are not indicated. In other words, each carbon atom is required to be associated with sufficient hydrogen atoms to offer the carbon atom with 4 bonds.
We do have all the chemical and molecular information about Cannabielsoic Acid A but we still lack a lot of information about the compound. We haven’t done the required research to know the medicinal effects of the compound on the human body just like other compounds present in the cannabis.
Cannabigerols
The first up in our study of cannabinodis is CBG (cannabigerol). Like CBD, CBG does not produce a “high” like THC does.
In fact, both THC and CBD start out as cannabigerol. It’s an interesting process. Basically, cannabis plants produce cannabigerol acid. Specific enzymes in the plant then breaks down the CBGA into the the acidic form of THC and CBD (known as THCA/CBDA). Next, THC and CBD form as the acid burns off via decarboxylation.
CBG works by increasing anandamide levels. Anandamide is an endocannabinoid, a naturally occurring cannabinoid found throughout our bodies, that helps regulate biological functions including appetite, sleep, and memory.
CBG Benefits:
Cannabigerol stimulates bone formation and healing. In a study published on pubmed.gov, “Age-related osteoporosis is characterized by reduced bone formation and accumulation of fat in the bone marrow compartment. Here, we report that the type 1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1) regulates this process.” Results showed they could stimulate bone marrow stem cells by regulating osteoblast (bone formation) and adipocyte (fat accumulation in connective tissue) differentiation in marrow stromal cells.
Slows tumor growth! CBD, CBG, and CBC were all shown to slow the progression and growth of tumors and cancer cells. In a study published by cannabisinternational.org, CBG and other cannabinoids seem to have anti-proliferative/pro-apoptotic effects.
CBG has shown to have anti-fungal and antimicrobial properties, which make it a candidate for antifungal and antibacterial treatment. Some scientists believe CBG could be part of an effective treatment against MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus), a highly prevalent antibiotic-resistant strain of bacteria.
CBG is also showing promising results for treating overactive bladder, Psoriasis skin treatment, Glaucoma, depression and anxiety, and neuroprotective effects
Cannabigerol Monomethyl Ether (CBGM) is a natural cannabinoid of the cannabigerol (CBG) group. Cannabinoids in the CBG group are placed together because they possess similar properties – properties that are almost the same as CBG. Like many other cannabinoids, we do not know much about CBGM.
Cannabis plants in North-East Asia seem to have the highest concentration of CBGM. In a particular study featuring cannabis plants grown in Sweden, it was discovered that seeds originating from South Africa have elevated levels of CBGM. However, whether this result was impacted by cross-pollination or was organic is not known.
CBGM was discovered in 1968 by researchers from the Kyushu University in Japan. The discovery was made after the compound was isolated from the Minamioshihara No. 1, a Japanese strain of hemp. It is one of only two ether cannabinoid compounds with an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl groups or two aryl groups.
What Are the Therapeutic Benefits of CGBM?
Beyond the molecular structure, no clear difference has been identified between the CBGM and other cannabinoids in the CBG group. It is possible that this compound may have similar effects on the human body as other cannabinoids. Due to the fact that CBGM is an ether compound, it may impact the body in ways that are unique and completely different than those of other cannabinoids. To glean some comprehensive knowledge of how CBGM may compare to CBG, similar strains are observed by scientists.
Cannabidiol (CBD) has a non-psychoactive counterpart known as cannabidivarin (CBDV). Both share a similar structure. They provide relief without giving the user any psychoactive effects, such as those given by tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). On the other hand, THC has tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) as its counterpart. THCV can oppose or neutralize the effects of THC, suppressing an individual’s appetite, rather than enhancing the hunger feeling. Even though we have given only two examples, it is an indication that similar cannabis compounds may have entirely different or entirely similar therapeutic benefits.
To understand the full therapeutic potential of CBGM, it is imperative that additional research be conducted. Presently, the therapeutic benefits of CBGM to the following medical conditions are a mere speculation. If CBGM does mimic CBG without any side effects, then it may help checkmate the following conditions:
Severe nausea
Glaucoma
Chronic pain
Crohn’s disease
Cancer
Arthritis
Psoriasis.
One of the most heavily researched areas in medicine is stem cells. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can differentiate into specific cell types. Depending on the way they are synthesized, a stem cell can turn into a heart cell or a skin cell or a brain cell. In fact, that is precisely what happens as a fetus develops into a newborn. Understanding human stem cells might help you understand why CBGA is such a uniquely important cannabinoid—CBGA functions kind of like a stem cell in the cannabis plant.
CBGA is the building block for the formation of THCa, CBDa, CBCa, and CBG. Notice that each of those (except for CBG) ends with an A? That’s because those cannabinoids are the acidic variations of the compounds. It is through decarboxylation, or the use of heat and oxidation, that the cannabinoids become activated. Heat and UV light cause these compounds to drop a molecule of carbon dioxide. THCA, for example, is not psychoactive until it is decarboxylated and synthesized into THC. Like THC, CBG is not created unless CBGA is activated through decarboxylation or oxidation. Though CBGA may have anti-proliferative (anti-cancer), anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic attributes, most of the research into the cannabinoid has gone into its essential role in the biosynthesis of other cannabinoids. This is an extremely important function, but the cannabinoid deserves far more research into its other medically significant attributes.
Without CBGA, there would be no THC, CBD, CBC, or CBG. In a way, this makes CBGA the most important of all of cannabis’ chemical compounds, especially given the centrality THC and CBD have taken in today’s discussion of cannabis’ place in our medicine. So here is a refresher on the cannabinoids CBGA is responsible for synthesizing, including two that are not nearly as researched as THC and CBD.
Molecular Formula – C23H34O4
Molecular Weight – 374.521 g/mol
Since Cannabigerolic acid Monomethyl ether belongs to Cannabigerolic category, there is a chance that CBGAM might contain some of the therapeutic or medicinal properties associated with CBG.
Even though the research in terms of specific cannabinoid CBG and its effects are still limited, restrictions associated with the testing of this plant make it more difficult to search volumes of quality and meaningful research with regards to Cannabigerol – CBG.
As per one of the Italian study that was published in the edition of Biological Psychology – May 2013, CBG – Cannabigerol contain strong anti-inflammatory properties and is capable of benefiting patients with IBD – inflammatory bowel disease.
It is also helpful in treating glaucoma as Cannabigerol has the potential to increase the drainage of fluid from the eye while reducing the pressure amount. Not to mention, the unique cannabinoid is also found to contain anti-depressant qualities while inhibiting the growth of the tumor.
Cannabigerovarin is a cannabinoid that does have psychotropic properties, meaning that it can aid THC’s psychoactive tendencies and effectiveness. Little is known about CBGV as it is a recently discovered cannabinoid.
What is known is that CBGV may help treat some cancers, like leukemia. It may help kill cancer cells and promote remission. It works with lysophosphatidylinositol (LSI) in the body as an endocannabinoid neurotransmitter. What this means is that it can help send chemical messages from one cell to another in the body.
CBGV may also aid LSI to regulate metabolic disorders like diabetes, obesity, insulin resistance, high blood pressure and high cholesterol. By increasing your abdominal metabolism, it may help decrease insulin resistance and formation of fat cells.
Additional potential benefits of CBGV in combination with LSI include:
Inflammation
Nervous system regulation
Atherosclerosis
Tumorigenesis
Additional research regarding CBGV is ongoing.
Is one of the major compounds in cannabis, and it targets receptors in our bodies that help regulate sleep patterns, appetite, and mood.
CBGVA slows down the rate of nerve degeneration and reduces the inflammation that accompanies irritable bowel disease. May also reduce the growth of cancer tumors.
Cannabinols and cannabinodiols
Is a psychoactive cannabinoid that is present in the plant Cannabis sativa at low concentrations. It is the fully aromatized derivative of cannabidiol (CBD) and can occur as a product of the photochemical conversion of cannabinol (CBN). Research is still underway to determine any potential health benefits
Cannabidivarin (CBDV) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that will not cause the euphoric feeling of being “high.” It is found more prevalently in indica strains, specifically landrace indica strains, and strains that are lower in tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Like CBD, CBDV significantly reduces the frequency and severity of seizures. It also reduces or even eliminates nausea associated with several conditions, and helps to reduce inflammation throughout the body. CBDV is also beneficial in the treatment of pain and mood disorders.
Is produced when THC is heated or exposed to oxygen. Unlike THC, Cannabinol does not bind well to CB1 and CB2 receptors. Scientists classify CBN as non-psychoactive. CBN is not an abundant cannabinoid. The CBN content found in the cannabis plant on average will be less than 1 percent.
Cannabinol (CBN) emerges when dried cannabis goes stale over time. When exposed to light or heat, THC gradually degrades into CBN, a non-psychoactive compound.
CBN Benefits:
Bone tissue growth. Studies show that CBN causes an indirect recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells that surround bone marrow. These stem cells are able to turn into bone and other tissues making it a possible candidate for healing bone fractures. The Journal of Neuroimmunology offers more information on this subject.
Like other cannabinoids, CBN is an anti-inflammatory cannabinoid that also has pain relief properties and preliminary research shows promise that CBN combined with CBD may prove to be an effective treatment for burns.
Sedative. According to a Royal Queen Seeds article, research shows that CBN can sometimes be as effective as pharmaceutical sedatives.
Scientists are also studying CBN as a possible sleep aid, an appetite stimulant, and as an anti-convulsive agent. CBN seems to work best symbiotically with CBD and THC.
Research has so far shown CBN to be therapeutically beneficial in the following ways:
Sleep aid – Of all the cannabinoids, CBN is the most sedative, making it a potential therapeutic option for those with insomnia, sleep apnea, or other sleep disorders. CBN and its derivatives have shown effective at significantly prolonging sleeping time in mice. Research suggests that sleeping improvements are even greater when CBN is combined with THC59.
Antibacterial – Evidence shows CBN could be an effective anti-bacterial. When applied topically, it was effective against MRSA5.
Pain relief – CBN has shown to be effective at reducing sensitivity to pain by stimulating the release of calcitonin gene-related peptide from sensory nerves. This pain relief response is performed without interacting with the CB1 and CB2 receptors, which suggests that CNB could provide even a stronger pain relief when used alongside CBD, which does lower pain through activation of the CB1 and CB2136.
Anti-inflammatory – CBN has shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, suggesting it could assist in the treatment of inflammatory diseases and disorders like multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, allergic asthma, and Crohn’s disease31.
Appetite stimulant – CBN has shown to increase appetite, which suggests it could assist in the treatment of cachexia and anorexia, and help improve eating desires in those with cancer or HIV/AIDS41.
Anti-convulsive – CBN has shown effective at significantly prolonging seizure latency in mice, suggesting it could assist in the treatment of epilepsy and other seizure disorders120,130.
Prevents glaucoma – CBN, when administered topically, has shown to considerably lower ocular tension, thus reducing the risk and progression of glaucoma27.
Bone stimulation – CBN is among the cannabinoids that are effective at stimulating bone growth51,52,92,110. As a result, CBN and other cannabinoids reduce the risk of osteoporosis and other bone diseases and support bone health.
Promotes the growth of healthy bone cells, anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-insomnia, and proven pain reliever.
One of the compounds present in cannabis plant is Cannabinol-C2 – CBN-C2. It is an ethanolic extract of the cannabis plant. The compound belongs to the Cannabinol – CBN category of Cannabis plant. Potential health benefits are still being researched.
Potential health benefits are still being researched.
Cannabinolic acid is the parent compound that decarboxylates into CBN. Curiously, in the plant, very little CBN is derived from CBN-A, and we do not see very much CBN-A in the plant; most CBN being derived from the oxidation of THC.CBN-A is anti-inflammatory, and likely anti-biological.
Potential health benefits are still being researched.
Cannabivarin, also interchangeably called cannabivarol or CBV, is the name for the chemical compound C19H22O2. It is a Divarin type and the second most abundant of the cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa. CBV is considered a non-psychoactive cannabinoid — it does not produce euphoric side effects like those, for instance, resulting from THC use. Cannabivarol is hardly present in fresh cannabis and is considered an oxidization product of tetrahydrocannabivarin, also called THCV. CBV also has a similar structure to CBN, or cannabinol, and many other phytocannabinoids. Cannabivarol is in the phytocannabinoids group, which contains other natural cannabinoids, including cannabigerol and cannabichromene. To determine the potential utility of CBV, we need further research on phytocannabinoids as a whole.
Cannabitriols
is one of the cannabinoids. It belongs to the category of cannabitriols. The research on this compound is yet to be done. Currently, we don’t have much information about 10-Ethoxy-9-hydroxy-delta-6a-tetrahydrocannabinol but we know that it is also used in composing skin treatments.
Just like other cannabinoids, 10-Ethoxy-9-hydroxy-delta-6a-tetrahydrocannabinol might also have some unique chemical properties which can only be known with progressive research work on these cannabinoids. For now, we can only assume that the compound holds the same therapeutic properties as that of cannabitriols.
Belongs to the category of cannabitriols. Until now, there has been no specific research work to understand this compound. Just like other compounds of the cannabis plant, 8, 9-Dihydroxy-delta-6a-tetrahydrocannabinol must also possess some unique chemical properties which are yet to be discovered.
Since it contains tetrahydrocannabinol, we can assume that the compound might contain some properties or effects similar to THC. Also, the compound belongs to cannabitriols so maybe it might show some promising effects similar to cannabitriols.
CBT actually hold the very similar structure as that of THC. is found only in small amounts of cannabis and it is yet to be discovered if this newly identified cannabinoid has any kind of euphoric effect or medicinal properties.
Potential health benefits are still being researched
Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinols
Delta-8-THC is chemically different from delta-9-THC by only a few atomic bonds and still offers a potent high of its own. While delta-8-THC only exists naturally in fractions of a percent, companies are finding value in concentrating esoteric cannabinoids for their unique effects and applications.
Delta-8- THC offers a unique, potent high all its own. Consumers of Delta-8-THC report experiencing pervasive body sensations, relaxation, and clear-headedness, with a lower psychotropic effect. Research shows that Delta-8-THC contains properties that may help reduce stress or tension, stimulate appetite, or reduce nausea
Potential health benefits are still being researched
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinols
THC is the most commonly known cannabinoid because it’s the psychotropic compound that produces the “high” that recreational cannabis users are seeking. While there is a risk of some negative side effects from THC, it is not possible to have a fatal overdose. Still, THC and cannabis are Schedule I controlled substances, which is a category of substances considered to be illegal according to the U.S. government.
You can only legally access THC if you are a registered medical cannabis patient in a state that has passed comprehensive medical cannabis legislation. Eight states have passed adult use cannabis laws and allow adults ages 21 and older to consume cannabis without a prescription or having to register with the stage.
Studies have found that THC is effective at managing nausea and vomiting, stimulating appetite, improving sleep, and providing pain relief.
THC has also demonstrated that it’s potentially beneficial for the treatment of the following diseases and disorders:
Alzheimer’s Disease – THC effectively lower levels of amyloid-beta peptide, the hallmark characteristic and key contributor to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Research has also shown it also enhances mitochondrial function, suggesting that THC could be therapeutically beneficial in treating Alzheimer’s disease through multiple functions21.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) – In several animal trials, THC has shown to delay the onset of ALS, prolong the survival of neurons, and slow the disease’s progression once it has manifested14,22,102. THC also reduces the pain, appetite loss, depression, and drooling symptoms associated with the disease3.
Anorexia – THC effectively stimulates hunger and increases pleasure when eating29. THC has also shown to increase average weight gain compared to a placebo4.
Arnold-Chiari Malformation and Syringomyelia – THC helps those with Arnold-Chiaro malformation and syringomyelia better manage the symptoms associated with their conditions. Studies have shown it significantly improves pain, sleep, and mood10,118,122.
Arthritis – THC has shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties and efficacy at fighting inflammation of the joints46. In addition, THC helps manage pain caused by joint diseases18.
Autism – THC has shown to significantly improve hyperactivity, lethargy, irritability, stereotypy, and inappropriate speech in an autistic child following regular treatments63. Additionally, THC’s activation of the CB2 receptors may be able to help restore neural communication and proper cell function43.
Bone Health – THC’s activation of CB2 receptors stimulates bone formation and inhibits bone breakdown8.
Cachexia – THC stimulates appetite in patients that have cachexia related to cancer56,89,90. It has also demonstrated to be effective at increasing appetite and stabilizing body weight in AIDS-cachexia patients11.
Cancer – THC has shown to possess anti-cancer properties, even reducing tumor sizes in the brain108. It is also proven effective at reducing both conditioned rejection and chemotherapy-induced nausea, allowing chemotherapy patients to more comfortably undergo treatments71. When combined with CBD, THC significantly reduces pain levels in cancer patients with intractable pain58. In cancer patients experiencing cachexia, THC has shown to significantly stimulate appetite56,89,90.
Crohn’s Disease / Irritable Bowel Syndrome – THC’s anti-inflammatory properties make it effective at combatting Crohn’s disease, even helping some patients achieve complete remission86. In addition, THC reduces the abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea symptoms associated with inflammatory bowel disease105.
Depression – THC has also been shown to decrease brain activity in response to negative stimuli, thereby helping to reduce the social withdrawal, apathy, inability to experience pleasure, and limited emotional expression associated with depression17.
Diabetes – THC reduces glucose intolerance, improves glucose tolerance, and increases insulin sensitivity to reduce the risk of diabetes123. In human studies, cannabis use has been correlated to a lower prevalence of diabetes100.
Leukemia – THC has been shown to kill leukemia cells99. Evidence also suggests that combining THC with other established cytotoxic agents further enhances leukemia cancer cell death72.
Lupus – THC’s anti-inflammatory properties makes it beneficial for treating inflammatory disorders like lupus87. THC also assists in the management of pain commonly associated with inflammation-related diseases and disorders26.
Migraines – THC effectively inhibits the pain response caused by migraines1,10,44.
Multiple Sclerosis – THC effectively reduces the pain associated with multiple sclerosis and provides relief from MS-related spasticity9,66,106.
Nail-Patella Syndrome – THC manages the pain associated with nail-patella syndrome10,85,97.
Nausea – Studies have found that cannabinoids, including THC, are effective at controlling nausea, and can prevent the anticipatory nausea experienced by chemotherapy patients94.
Obesity – The exposure to THC in cannabis smoke has found to be associated with a lower rate of obesity compared to non-cannabis users67.
Pain – THC has been shown effective for lowering pain levels associated with a wide variety of conditions, including spasticity, headache, migraines, and other acute pain and chronic pain conditions10,57.
Parkinson’s Disease – THC shown to help prevent damage caused by free radicals and that it activatesa receptor to encourage mitochondria formation, thus helping in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease132. In addition, smoking cannabis has shown to significantly improve motor disability and impairments, tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, sleep and pain in Parkinson’s disease patients74.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) – Cannabis use has been shown to significantly reduce PTSD symptoms45. Users with PTSD experience better sleep and fewer nightmares13. Studies suggest that cannabis has the potential to dampen the strength and emotional impact of traumatic memories95. In addition, administering THC shortly after a traumatic event can help prevent the development of PTSD-like symptoms20.
Sickle Cell Anemia – Cannabis and THC have proven effective at lowering pain associated with sickle-cell anemia61. In addition, THC’s anti-inflammatory properties can help minimize the vascular occlusion and tissue infarction commonly caused by the disorder111.
Spasms – THC has shown effective for significantly improving muscle spasticity16,113.
Spinal Cord Disease – Cannabis (THC) can improve the pain, sleeping problems, bladder control, spasticity, muscle twitching, and depression commonly associated with spinal cord diseases3,22. In addition, animal trials have demonstrated that cannabinoids can prolong the survival of neurons and slow the progression of spinal cord diseases14.
Spinal Cord Injuries – THC has shown to reduce swelling and compression lesion volume, and help preserve white matter and myelin when administered shortly after a spinal cord injury6,48. It’s also been shown to improve locomotor functional recovery64.
Traumatic Brain Injury – By interacting with the CB1 and CB2 receptors, THC stimulates the release of minocycline, which reduces brain swelling and neurological impairment, and diffuses further injuries to the brain’s axons following a TBI73. In addition, one study found that when individuals have detectable levels of THC in their bloodstream, they are less likely to die as a result of a traumatic brain injury91.
Tetrahydrocannabinol-C4, also known as THC-C4 and butyl-THC, is a homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the active component of cannabis. They are only different by the pentyl side chain being replaced by a butyl side chain. It is unknown whether THC-C4 is an agonist, partial agonist, or antagonist at the cannabinoid receptors. The propyl analog, THCV, is a cannabinoid receptor type 1 and cannabinoid receptor type 2 antagonist, while THC is a CB1 agonist. THC-C4 has rarely been isolated from cannabis samples, but appears to be less commonly present than THC or THCV. It is metabolised in a similar manner to THC.Similarly to THC, it has 7 double bond isomers and 30 stereoisomers.
THCA is commonly being used as a nutritional supplement and dietary enhancement for its prospective:
Anti-inflammatory properties
Antidiabetic properties
Neuroprotective properties
Antispasmodic properties
Antiemetic properties (increasing appetite and decreasing nausea)
Possess greater stability and crystallizes much more readily than the former THCA-A. This makes THCA-B, an important molecule for major modeling studies of several cannabinoid receptors.
Is a precursor of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the active component of cannabis.
THCA is found in variable quantities in fresh, undried cannabis, but is progressively decarboxylated to THC with drying, and especially under intense heating such as when cannabis is smoked or cooked into cannabis edibles. THCA is often the majority constituent in cannabis resin concentrates, such as hashish and hash oil, when prepared from high-THC cannabis plant material, frequently comprising between 50% and 90% by weight.
Potential health benefits are still being researched
One of the THC acidic forms
Both THC and THCV are psychoactive and will cause the user to get “high.” When THC binds to the body’s CB1 and CB2 receptors it activates them initiating the “high” effect. At low doses THCV also binds to those same receptors, but it does not activate them, behaving more like CBD. At higher dosages, THCV will activate the CB1 receptor much like THC and will produce a psychoative “buzz.”
The feeling THCV produces seems to come on faster than THC and fades out faster as well. Users report a more clear-headed and stimulating high.
THCV Benefits, according to Leafly’s Bailey Rahn:
THCV may have anti-convulsive properties and can raise the seizure threshold for those with epilepsy. As a result, they experience fewer seizures.
Researchers are studying THCV’s ability to stimulate bone growth as a potential treatment for osteoporosis and other bone conditions.
THCV counteracts feelings of anxiety and shown to be effective in PTSD treatment.
Improves motor control, reduce tremors, and lessen the effects of brain lesions caused by Alzheimer’s disease. However it’s important to know that research is in the early stages and much more information is still needed.
Researchers believe THVC blocks the rewarding sensations we experience when eating, especially the unhealthy, comfort foods.
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabivarinic acid (THCVA)
Miscellaneous cannabinoids
The following are other cannabinoids not classified in a class, or those we’re not sure what class they fit into.
10-Oxo-delta-6a-tetrahydrocannabinol (OTHC)
Miscellaneous
Potential health benefits are still being researched
Potential health benefits are still being researched
Potential health benefits are still being researched
Potential health benefits are still being researched
Potential health benefits are still being researched
Potential health benefits are still being researched
Potential health benefits are still being researched
Potential health benefits are still being researched
Potential health benefits are still being researched
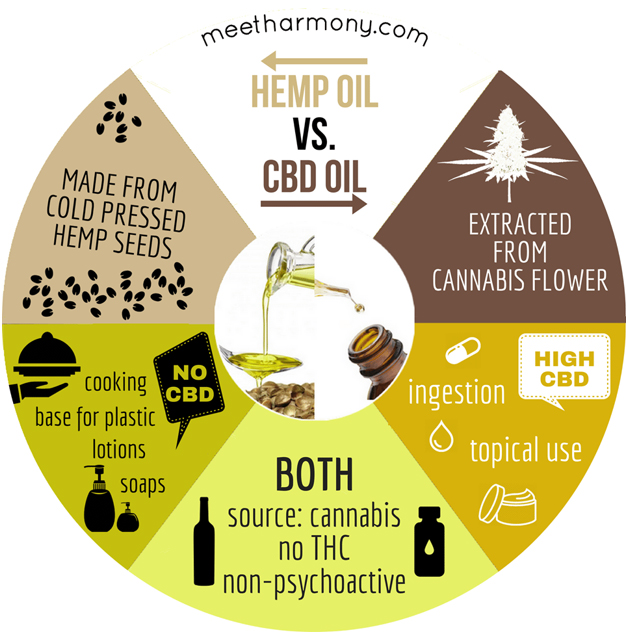
What is Hemp Oil?
Hemp seed oil (or hemp oil) is a nutritious type of edible culinary oil made from hemp seeds whereas CBD comes from the plant itself with most of the cannabinoids in the flowers.
Hemp plants are a form of cannabis sativa that is typically grown for industrial purposes. These plants contain low levels of cannabinoids including the two most commonly known: THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol). The oil is extracted from the hemp plants by pressing the seeds they produce. This method of extraction is similar to how olive and coconut oil is obtained.
Since hemp seeds do not contain any THC, the extracted oil does not contain any as well. Trace amounts may potentially still be found due to plant matter adhering to the seeds during processing. However, modern commercial manufacturing decontaminates seeds by 99.99%.
Hemp Oil is relative to many other carrier oils—along the lines of sunflower seed oil and jojoba oil—in that it’s a cold-pressed extract from seeds. Hemp seed oil, sometimes referred to as cannabis sativa seed oil, is perfectly good seed oil that’s high in antioxidants, omega-3 and -6 fatty acids
Often described as a “superfood,” hemp seed oil is packed with vital nutrients, including amino acids, fiber, Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, as well as an array of important vitamins and minerals, but contains no CBD. This makes hemp seed oil a valuable addition to any diet, especially those that may be nutrient deficient.
Hemp oil is often used in shampoos, lotions, soaps, and other beauty or cosmetic products around the world. It can also be found as an ingredient in plastics, paint, dressings, lubrications, and bio-diesel fuel. As such, using hemp oil can be an experience individuals desire since it has so many benefits.
Benefits of Hemp Oil
The fatty acids hemp oil contains (omega-3 and omega-6) is one of the most beneficial health factors of it. These acids can help diminish the signs of aging and improve heart health. They also are what make hemp oil such a great moisturizer, since omega-3 and omega-6 act in a similar manner as the skin’s natural lipids6. This allows an increase of skin elasticity and water retention. It is great to use hemp oil to hydrate your skin, hair, and nails, helping them stay healthy and strong.
Cholesterol can also be lowered by consuming fatty acids6. They help to increase your metabolism, which results in burning fat at a faster rate and keeping it from depositing on your artery wall. Your nerve cells are also protected by omega-3 and omega-6, as they prevent the damage of the myelin sheath.
Gamma linoleic acid, found in hemp oil, helps to fight psoriasis, a skin condition that affects many individuals around the world. Learn more about how hemp seed oil helps your face and psoriasis.
Again, keep in mind when looking at hemp oil vs CBD oil, that some hemp oils can also contain CBD, depending on the type oil purchased. Read the label to ensure that you are getting the type of oil that you desire.
and is commonly used as a substitute for traditional cooking oils with the exception of deep-frying. This hemp oil is also commonly infused into body care products to nourish the skin, nails, and hair.